Shell
shell是一个命令行工具.在操作系统中,内核直接与硬件进行交互,并由操作系统在内核的基础上封装了调用硬件的接口.应用程序和服务再调用接口进行运行.
shell就是内核与用户直接交互的工具,linux中默认使用的终端默认为BASH解释器来执行shell命令.
帮助命令
# 命令的格式-命令不能完全满足工作需要,因此需要参数辅助
命令名称 [命令参数] [命令对象]
# 查看man命令的帮助
man --help
man -h命令参数的长格式与短格式:
- 短格式使用
-开头,后边跟参数的缩写 ;长格式使用--开头,后边跟完整的单词 长短格式参数合并原则:
- 只有短格式能与短格式合并,合并后保留一个减号,有时减号也可以省略
- 短格式与长格式之间不能合并
常用系统工作命令
输出字符串
echo [需要输出的字符串]输出时间
# 打印当前时间 date # 格式化输出时间 date ["+参数"] # 例如:输出格式化的时间 date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"参数 作用 %Y 年 %m 月 %d 日 %H 小时(24小时制) %I 小时(12小时制) %M 分钟 %S 秒 %j 今天是当年第几天 重启
reboot关机
# 以下三个命令都可以立刻关机 poweroff halt shutdown -h now init 0 # 延时关机(10分钟后) shutdown -h 10下载
wget [参数] [下载地址]参数 作用 -b 后台下载模式 -P 下载到指定目录 -t 最大尝试次数 -c 断点续传 -p 下载页面内的所有资源 -r 递归下载 查看进程状态
ps [参数]参数 作用 -a 显示所有 -u 显示用户及其他详细信息 -x 显示没有控制终端的进程 linux进程主要包括以下进程状态:
状态 状态 解释 R 运行 进程正在运行或队列中等待运行 S 中断 进程处于休眠中,当某个条件形成或者接受到信号则脱离该状态 D 不可中断 进程不响应系统状态,kill也不能将其杀掉 Z 僵死 进程已经终止,但是描述符依然存在,等待父进程将其释放 T 停止 进程接受到停止信号后会停止运行 动态监视进程状态
top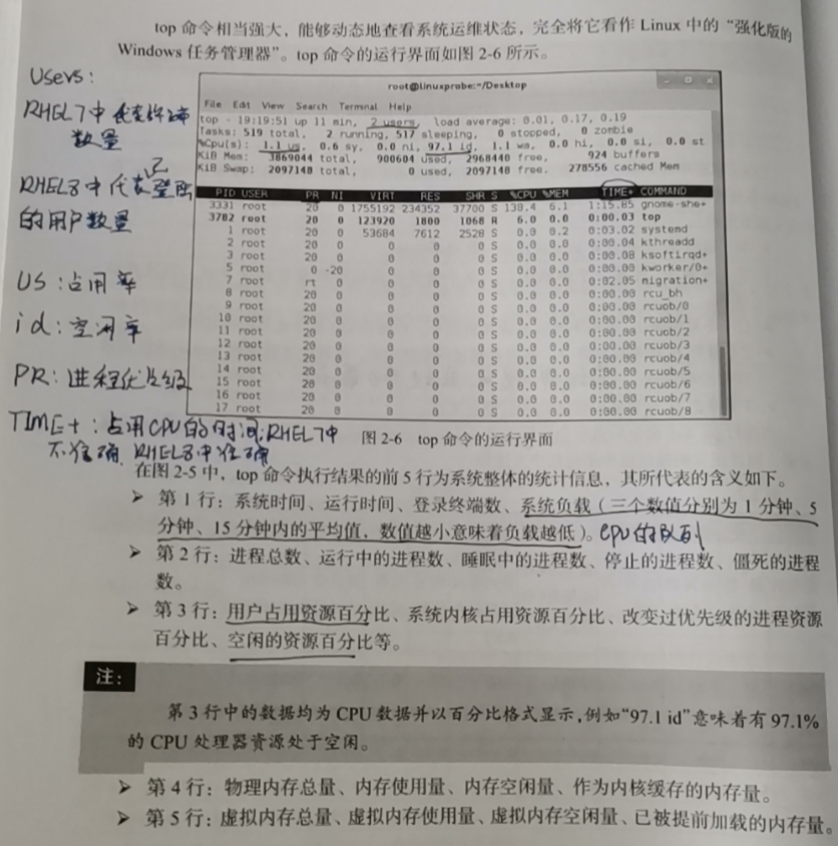
如果我们执行一个命令后想立即停止它,那么我们使用crtl+c,如果想让一个命令在后天进行,那么我们在最后加一个&符号。
pidof命令
用来查询某个指定服务进程的PID
pidof [参数] [服务名称]kill命令
终止指定PID的进程
kill [参数] [进程PID]killall
终止某个服务的全部进程
pidof [参数] [服务名称]
### 系统状态检测命令
- ifconfig
uname命令
可以用来查看系统内核和系统版本等信息
# -a 可以显示更多的详细信息 uname [-a]
uptime命令
可以显示系统的:当前时间信息、运行时间、用户数量、负载情况
uptime >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# uptime 09:59:53 up 5 min, 2 users, load average: 0.05, 0.24, 0.14free命令
# -h 代表人类易读,会第结果添加单位 free [-h] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# free total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 7953688 229928 7383272 10232 340488 7468988 Swap: 0 0 0 [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 7.6Gi 223Mi 7.0Gi 9.0Mi 332Mi 7.1Gi Swap: 0B 0B 0Bwho命令,也可以使用w
用户查看当前登入主机的用户终端信息
who [参数] >>> [root@localhost ~]# who root tty2 2021-01-17 19:32 (tty2) [root@localhost ~]# w 19:32:56 up 1 min, 1 user, load average: 1.65, 0.50, 0.17 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root tty2 tty2 19:32 1:02 6.65s 0.12s /usr/libexec/tracker-minelast命令
用于查看系统的登录记录,当由于这些信息是以文件的方式保存在日志中,因此可以被修改
last [参数] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# last root pts/1 117.184.158.82 Fri Jan 15 09:56 still logged in root pts/0 117.184.158.82 Fri Jan 15 09:56 still logged in reboot system boot 4.18.0-240.1.1.e Fri Jan 15 09:54 still running wtmp begins Sat Dec 12 19:26:57 2020history命令
可以用来查看用户的命令输入记录
# 查看记录 history # 清空记录 history -c # 还可以通过历史记录的编号来执行对应的命令 ![历史记录的编号] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# uname Linux [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# history 1 2021-01-15 10:15:26 root history 2 2021-01-15 10:15:35 root uname 3 2021-01-15 10:15:38 root history [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# !2 uname Linuxsosreport
用于手机系统的所有配置信息,并输出诊断文档
sosreport
工作目录切换命令
pwd
显示用户当前所在目录
pwd >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# pwd /rootcd
切换用户的目录,当没有参数是,代表返回上一级目录
# 切换到指定目录 cd [目录名称] # 切换到上一次所处目录 cd - # 切换到上级目录 cd.. # 切换到当前用户的家目录 cd ~ # 切换到其他用户的家目录 cd ~[用户名] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cd /etc [root@ecs-3511-0003 etc]# cd ~ [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cd /bin [root@ecs-3511-0003 bin]# cd - /root [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# pwd /rootls命令
显示目录中的文件信息,蓝色的为文件夹,白色字的为文件。
# -a 显示所有文件(包括隐藏文件) # -l 显示文件的属性 ls [选项][文件] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls -a . .. .bash_history .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .config .cshrc .history .ssh .tcshrc .viminfo [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls -al total 40 dr-xr-x---. 4 root root 4096 Jan 15 09:56 . dr-xr-xr-x. 20 root root 4096 Jan 15 09:55 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 12 19:26 .bash_history -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18 May 11 2019 .bash_logout -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 May 11 2019 .bash_profile -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 176 May 11 2019 .bashrc drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Jan 15 09:56 .config -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 100 May 11 2019 .cshrc -rw------- 1 root root 0 Dec 12 19:26 .history drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Jan 15 09:55 .ssh -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 129 May 11 2019 .tcshrc -rw------- 1 root root 532 Dec 12 19:26 .viminfotip:
ls -l 效果与ll一样
文本文件编辑命令
cat命令
查看文件,查看长内容文件时,内容会直接滚到最底部
# -n 显示行号 cat [选项][文件] [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cat -n .bash_logout 1 # ~/.bash_logout 2more命令
用来查看内容比较长的文件,可以使用空格进行翻页,使用回车进行
more 文件名head命令
用于查看纯文本文档的前N行
head [参数]文件名 # 查看前20行 head -n 20 文件名tail命令
用户查看文件的后N行,也可以实时刷新
tail [参数][文件] # 查看后5行 tail -n 5 /var/log/messages # 查看文件最后的内容,并实时刷新 tail -f /var/log/messagestr命令
替换文本文件中的字符
tr [原始字符][目标字符] # 在显示的时候将文件内的小写字符显示为大写,但不修改原文件的内容 cat /var/log/messages | tr [a-z] [A-Z]wc命令
显示文本的行数、字数、字节数,统计汉字时有问题
wc [参数] 文本 # 查看系统中的用户数量 wc -l /etc/passwd >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# wc /var/log/messages 1476 16193 141535 /var/log/messages [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd 25 /etc/passwd参数 作用 -l 只显示行数 -w 只显示字数 -c 只显示字节数 stat命令
查看文件的存储信息和时间信息
stat 文件名称 >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# stat /etc/passwd File: /etc/passwd Size: 1237 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 2100898 Links: 1 Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root) Access: 2021-01-15 09:55:11.170998648 +0800 Modify: 2020-12-12 19:16:44.189164859 +0800 Change: 2020-12-12 19:16:44.199164859 +0800 Birth: -tip:
- ATIME 最后一次访问文件内容的时间
- MTIME最后一次修改文件内容的时间
- CTIME最后一次修改文件属性的时间
cut 命令
用于通过’列‘来提取文本字符
cut [参数] 文本 cut [-d间隔符号] [-f列数] 文本 >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# head -n1 /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd root bin daemon ...diff命令
diff [参数]文件 # 比较两个文件是否相同 diff --brief 文件1 文件2 # 查看两个文件的差异 diff -c 文件1 文件2 >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cat a.txt Welcome to linuxprobe.com Red Hat certified Free Linux Lessons Professional guidance Linux Course [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cat b.txt Welcome tooo linuxprobe.com Red Hat certified Free Linux LeSSonS ////////.....//////// Professional guidance Linux Course [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# diff --brief a.txt b.txt Files a.txt and b.txt differ [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# diff -c a.txt b.txt *** a.txt Fri Jan 15 13:51:05 2021 --- b.txt Fri Jan 15 13:52:54 2021 *************** *** 1,5 **** ! Welcome to linuxprobe.com Red Hat certified ! Free Linux Lessons Professional guidance Linux Course --- 1,7 ---- ! Welcome tooo linuxprobe.com ! Red Hat certified ! Free Linux LeSSonS ! ////////.....//////// Professional guidance Linux Course
文件目录管理命令
touch命令
创建空白文件或者设置文件的时间
touch [参数][文件] >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# stat a.txt File: a.txt Size: 98 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 262160 Links: 1 Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root) Access: 2021-01-15 13:51:59.074276326 +0800 Modify: 2021-01-15 13:51:05.269279533 +0800 Change: 2021-01-15 13:51:05.274279532 +0800 Birth: - [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# echo "Visit the LinuxProbe.com to learn linux skills" >> a.txt [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# stat a.txt File: a.txt Size: 145 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 262160 Links: 1 Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root) Access: 2021-01-15 13:51:59.074276326 +0800 Modify: 2021-01-15 14:09:39.434213123 +0800 Change: 2021-01-15 14:09:39.434213123 +0800 Birth: - [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# touch -d "2021-01-15 13:51:05.269279533" a.txt [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# stat a.txt File: a.txt Size: 145 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 262160 Links: 1 Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root) Access: 2021-01-15 13:51:05.269279533 +0800 Modify: 2021-01-15 13:51:05.269279533 +0800 Change: 2021-01-15 14:10:28.142210220 +0800 Birth: -参数 作用 -a 修改’读取时间‘(atime) -m 修改’修改时间‘(mtime) -d 同时修改’读取时间‘与’修改时间‘ mkdir命令
可以创建目录
mkdir [参数] 目录名 mkdir c # -p 参数可以递归创建文件夹 mkdir -p a/b/ccp命令
用来复制文件或者文件夹,复制的时候分为三种情况:
- 如果目标文件是目录,则会把源文件复制到目录中
- 如果目标文件是已存在的文件,则会询问是否覆盖
- 如果目标文件不存在,则执行正常的复制操作
cp [选项] 源文件 目标文件 >>> [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls a.txt b.txt [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cp a.txt cp: missing destination file operand after 'a.txt' Try 'cp --help' for more information. [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cp a.txt a-1.txt [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls a-1.txt a.txt b.txt [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cp a.txt a-1.txt cp: overwrite 'a-1.txt'? 1 [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# ls a-1.txt a.txt b.txt
| 参数 | 作用 |
| ---- | -------------------------------------------- |
| -p | 保留原始文件的属性 |
| -d | 若对象为“链接文件”,则保留该“链接文件”的属性 |
| -r | 递归持续复制(用于目录) |
| -i | 若目标文件存在则询问是否覆盖 |
| -a | 相当于-pdr(p、d、r为上述参数) |
mv命令
剪切文件或者将文件进行重命名,会将源文件删除
mv [选项] 源文件 [目标路径|目标文件名]rm命令
用户删除文件或目录
rm [选项] 文件 # -r 删除目录需要加此参数 # -f 强制删除,不需要用户进行二次确认dd命令
按照指定大小和个数的数据块来复制文件或者转换文件
dd [参数]参数 作用 if 输入的文件名称(input file) of 输出的文件名称(output file) bs 设置每个“块”的大小 count 设置要复制“块”的个数 file命令
查看文件的类型
file 文件名
打包压缩与搜索
tar 命令
用于对文件进行打包压缩或者解压
tar [选项][文件] >>> [root@localhost c]# tar -cvf a.tar.gz a.txt a.txt [root@localhost c]# ls a.tar.gz a.txt [root@localhost c]# mkdir d [root@localhost c]# tar -xvf a.tar.gz -C ./d a.txt [root@localhost c]# ls a.tar.gz a.txt d参数 作用 -c 创建压缩文件 -x 解开压缩文件 -t 查看压缩包内有哪些文件 -z 用Gzip压缩或解压 -j 用bzip2压缩或解压 -v 显示压缩或解压的过程 -f 目标文件名(解压缩压缩的) -p 保留原始的权限与属性 -P 使用绝对路径来压缩 -C 指定解压到的目录 tip:
- 一般使用的时候都带-v 参数,来展示过程
- -f 需要写在参数最后边
grep
在文本中执行关键词搜索,并显示匹配结果.如果想搜索的关键字中有空格,则需要给关键字加引号
grep [选项][文件] [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# cat a.txt Welcome to linuxprobe.com Red Hat certified Free Linux Lessons Professional guidance Linux Course Visit the LinuxProbe.com to learn linux skills [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# grep pro a.txt Welcome to linuxprobe.com [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# grep -c pro a.txt 1 [root@ecs-3511-0003 ~]# grep -nv pro a.txt 2:Red Hat certified 3:Free Linux Lessons 4:Professional guidance 5:Linux Course 6:Visit the LinuxProbe.com to learn linux skills
| 参数 | 作用 | | ---- | ---------------------------------------------- | | -b | 将可执行文件(binary)当作文本文件(text)来搜索 | | -c | 仅显示找到的行数 | | -i | 忽略大小写 | | -n | 显示行号 | | -v | 反向选择——仅列出没有“关键词”的行。 | 3. find命令 用来按照指定条件查找文件find [查找路径] 寻找条件 操作
# 查看当前目录下的文件
find . -name a.txt
# 将查找到的文件复制到另外一个文件夹中
# 操作默认为print ,可以使用 -exec进行其他操作的处理
>>>
[root@localhost ~]# find . -name a.txt
./a.txt
[root@localhost ~]# find . -name a.txt -exec cp -a {} ./c/ \;
cp: './c/a.txt' and './c/a.txt' are the same file
> tip:
>
> -exec 中{}代表find命令查找到的结果,命令的结尾必须是 `\;`
| 参数 | 作用 |
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| -name | 匹配名称 |
| -perm | 匹配权限(mode为完全匹配,-mode为包含即可) |
| -user | 匹配所有者 |
| -group | 匹配所有组 |
| -mtime -n +n | 匹配修改内容的时间(-n指n天以内,+n指n天以前) |
| -atime -n +n | 匹配访问文件的时间(-n指n天以内,+n指n天以前) |
| -ctime -n +n | 匹配修改文件权限的时间(-n指n天以内,+n指n天以前) |
| -nouser | 匹配无所有者的文件 |
| -nogroup | 匹配无所有组的文件 |
| -newer f1 !f2 | 匹配比文件f1新但比f2旧的文件 |
| --type b/d/c/p/l/f | 匹配文件类型(后面的字幕字母依次表示块设备、目录、字符设备、管道、链接文件、文本文件) |
| -size | 匹配文件的大小(+50KB为查找超过50KB的文件,而-50KB为查找小于50KB的文件) |
| -prune | 忽略某个目录 |
| -exec …… {}\; | 后面可跟用于进一步处理搜索结果的命令 |